本次示例是红黑树使用测试。
libhl开源库编译安装过程,参看往期文章:https://www.madbull.site/?p=897 C语言实现基础数据结构库
注意:此红黑树 不是线程安全的。
所以在多线程使用时,如果同时涉及读写,则需要上锁或者通过无锁编程实现互斥访问;
如果把数据一次性且是单线程加载到红黑树中,然后不再修改,此后只读取数据,则不用考虑互斥的问题。
测试代码
示例把 /etc/os-release 文件每一行去掉换行符 \n 后,计算哈希值,每一行数据写入到红黑树中,涉及到 红黑树创建、数据增加、数据查询、数据删除、红黑树遍历和红黑树销毁操作。
本文对数据做哈希算法使用的 cityhash,具体用法参看往期文章:https://www.madbull.site/?p=1322 cityhash–对字符串的哈希算法
创建.c文件 rbttst.c,内容如下:
// gcc -Wall -o rbttst rbttst.c -lhl -lcityhash
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include "cityhash.h"
#include "rbtree.h"
#include "comparators.h"
const char * filepath = "/etc/os-release" ;
// 对数据 计算哈希值 作为key,把对应的 data 存入到 rbt 的一个节点中。
int rbt_add_data( char * data, size_t data_size, rbt_t * rbt_p ) {
uint64 key = CityHash64(data, data_size);
// 1、key 的空间不需要保留,rbt_add不需要key的空间
// 2、data 的空间需要保留,data指针直接赋值给了 rbt_node_t 结构的 void *value 字段
// 3、如果 key 已经存在,则自动删除 rbt 里的旧数据,把新数据重新加入到 rbt 中
rbt_add(rbt_p, &key, sizeof(uint64), data);
return 0 ;
}
// 对数据 计算哈希值 作为key,并删除此节点
int rbt_del_data( char * data, size_t data_size, rbt_t * rbt_p ) {
// void * value = NULL ; // 接收删除节点的 value 指针指向的空间
// 计算 key
uint64 key = CityHash64(data, data_size);
// 从 rbt 红黑树里查询到 key 之后,再删除此数据。
// 如果 void ** value 参数给的是NULL,则会自动调用 内存释放函数,释放 rbt_node_t 中存值的空间。
// 否则,会把 rbt_node_t 中value指向的空间地址,赋值给value指针,
int ret = rbt_remove(rbt_p, &key, sizeof(uint64), NULL);
if ( ret == 0 ) {
printf("%s:%s : remove node key[%lu] value[%s]\n", __FILE__, __func__, key, data) ;
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "%s:%s : can not find key[%lu] value[%s]\n", __FILE__, __func__, key, data) ;
}
return ret ;
}
// 从文件中读取数据,每一行条数据,存入到 rbt--红黑树中
int file_to_rbt(const char * filepath, rbt_t * rbt_p ) {
FILE * fd = NULL ;
char read_buf[2048] ;
char * data = NULL ;
size_t data_len = 0 ;
// 1、 打开文件
fd = fopen( filepath, "r") ;
if ( fd == NULL ) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s:%s : open file [%s] error !", __FILE__, __func__, filepath) ;
return -1 ;
}
// 2、逐行读取数据,并加入到 rbt 红黑树中。
memset(read_buf, 0x00, sizeof(read_buf) ) ;
while (fgets(read_buf, sizeof(read_buf), fd) != NULL ) {
// 计算长度
data_len = strlen(read_buf) ;
// 处理换行符号
if ( '\n' == read_buf[data_len-1] ) {
read_buf[data_len-1] = '\0' ;
}
// 创建 rbt_node_t 结构中 value 指针指向的数据
data = (char *)calloc(1, data_len) ;
memcpy(data, read_buf, data_len) ;
rbt_add_data(data, data_len, rbt_p) ;
memset(read_buf, 0x00, sizeof(read_buf) ) ;
}
fclose(fd) ;
return 0 ;
}
// 测试 查询 功能
int rbt_search_data( char * data, size_t data_size, rbt_t * rbt_p ) {
int ret = 0 ;
uint64 key = CityHash64(data, data_size);
char * value = NULL;
ret = rbt_find(rbt_p, &key, sizeof(uint64), (void**)&value);
if( ret == 0 ) {
printf("%s:%s : key[%lu] value[%s]\n", __FILE__, __func__, key, value) ;
return 0 ;
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "%s:%s : can not find key[%lu] value[%s]\n", __FILE__, __func__, key, value ) ;
return -1 ;
}
}
void my_free(void *v) {
printf("%s:%s : value = [%s] delete\n", __FILE__, __func__, (char *) v) ;
free(v) ;
}
rbt_walk_return_code_t walk_cb(rbt_t *rbt, void *key, size_t klen, void *value, void *priv) {
static int i = 0 ;
char * prestr = (char *)priv ;
++i ;
printf("%s:%s %s: i[%d] walk key[%lu] value[%s]\n", __FILE__, __func__, prestr, i, *(uint64 *)key, (char *) value ) ;
return RBT_WALK_CONTINUE ;
}
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {
rbt_t * rbt_p = NULL ;
// 测试创建
rbt_p = rbt_create( libhl_cmp_keys_int64, my_free);
// 测试添加数据
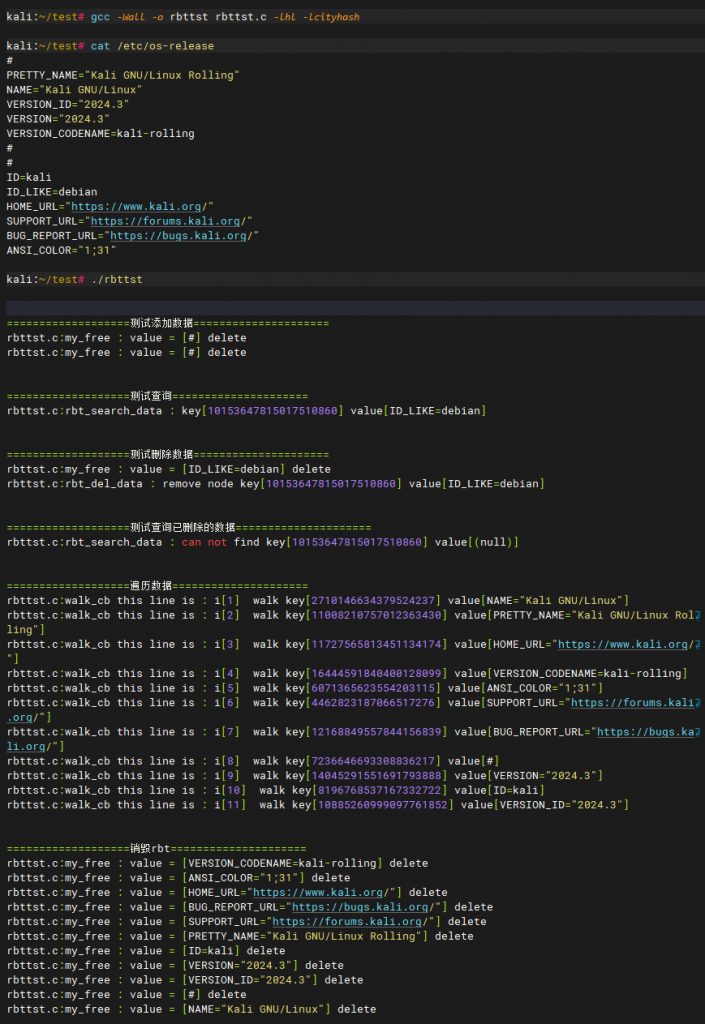
printf("\n\n===================测试添加数据=====================\n" ) ;
file_to_rbt(filepath, rbt_p ) ;
// 测试查询
printf("\n\n===================测试查询=====================\n" ) ;
char * test1 = "ID_LIKE=debian" ; // 从 filepath 文件中随便找了一行作为测试项
rbt_search_data( test1, strlen(test1)+1, rbt_p ) ;
// 测试删除数据
printf("\n\n===================测试删除数据=====================\n" ) ;
rbt_del_data( test1, strlen(test1)+1, rbt_p ) ;
// 测试查询一个已经删除的数据
printf("\n\n===================测试查询已删除的数据=====================\n" ) ;
rbt_search_data( test1, strlen(test1)+1, rbt_p ) ;
// 遍历整个rbt
printf("\n\n===================遍历数据=====================\n" ) ;
char * pre = "this line is " ;
rbt_walk(rbt_p , walk_cb, pre) ;
// 销毁 , 会自动调用 my_free
printf("\n\n===================销毁rbt=====================\n" ) ;
rbt_destroy(rbt_p);
return 0 ;
}编译测试
编译指令:gcc -Wall -o rbttst rbttst.c -lhl -lcityhash
1、在创建数据时,相同哈希的数据,会用新数据把旧数据更新,同时销毁旧数据;
2、添加数据、查询数据、删除数据,这三个操作中,哈希的计算方法和提供的数据要完全一致。如果提供的数据结构中包含指针,确保指针值一致。
3、自测红黑树遍历存在BUG,遍历的回调函数返回 RBT_WALK_CONTINUE 时好使,其他返回值不好使。这是因为红黑树调整以及数据递归遍历导致的,还需要修改libhl的开源的代码才可以,以后用空了调试调试再更新。


发表回复