之前介绍过getopt函数解析命令行,参看往期文章:https://www.madbull.site/?p=1606
今天做个getopt_long的笔记。
函数定义
函数原型在 getopt_ext.h 文件中的定义:
extern int getopt_long (int ___argc, char *__getopt_argv_const *___argv,
const char *__shortopts,
const struct option *__longopts, int *__longind)其中参数 struct option 结构的定义如下:
struct option
{
const char *name;
/* has_arg can't be an enum because some compilers complain about
type mismatches in all the code that assumes it is an int. */
int has_arg;
int *flag;
int val;
};- name:参数名称,不需要加 “–”
- has_arg:有三种类型,如下:
- no_argument 0 参数不需要选项
- required_argument 1 参数必须要带选项
- optional_argument 2 参数可以带选项也可以不带选项
- flag:把值直接复制给*flag变量
- val:当
flag != NULL时,直接把 val 值赋值给*flag变量;当flag == NULL时,则val作为getopt_long函数的返回值。 - 另外:全局变量 optarg 在带选项的参数里,作为选项值。
使用举例
// gcc getoptlong.c -o test
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <getopt.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int opt;
int verbose = 0;
char *output_file = NULL;
int count = 1; // 默认值
// 定义长选项
struct option long_options[] = {
{"verbose", no_argument, &verbose, 1}, // 无参数
{"output", required_argument, 0, 'o'}, // 必须参数
{"count", optional_argument, 0, 'c'}, // 可选参数
{0, 0, 0, 0}
};
while ((opt = getopt_long(argc, argv, "o:c::", long_options, NULL)) != -1) {
switch (opt) {
case 0:
// 已通过 flag 设置 verbose
break;
case 'o':
output_file = optarg;
printf("输出文件: %s\n", output_file);
break;
case 'c':
if (optarg) {
count = atoi(optarg);
printf("自定义计数: %d\n", count);
} else {
printf("使用默认计数: %d\n", count);
}
break;
case '?':
printf("未知选项或缺少参数\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
// 打印最终结果
printf("\n最终配置:\n");
printf("详细模式: %s\n", verbose ? "开启" : "关闭");
printf("输出文件: %s\n", output_file ? output_file : "无");
printf("计数: %d\n", count);
return 0;
}编译测试
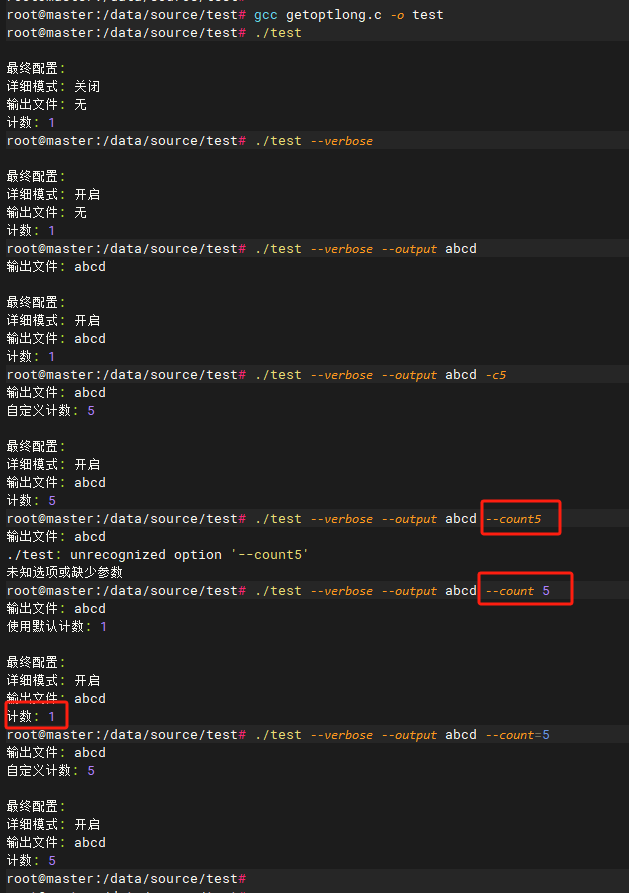


发表回复